 Medically, muscle tone is simply the tension existing in the muscles naturally. Humans have muscle tone; and its importance is to give you a perfect overall look, more energy, balance and posture, confidence, and even control the development of certain diseases.
Medically, muscle tone is simply the tension existing in the muscles naturally. Humans have muscle tone; and its importance is to give you a perfect overall look, more energy, balance and posture, confidence, and even control the development of certain diseases.
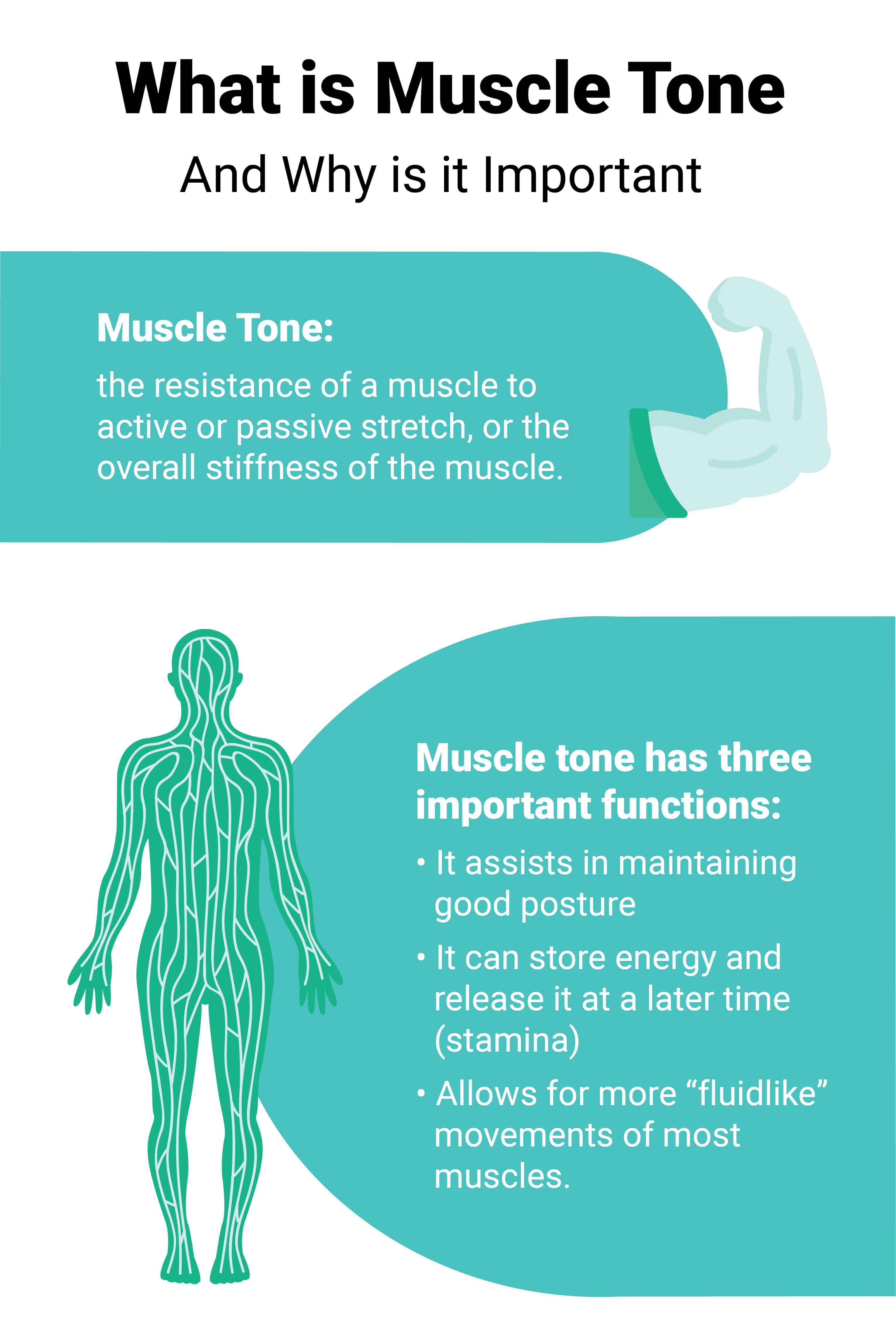
In physiology, muscle tone is the resistance of muscles to passive stretch during a relaxing state and also the low-level contraction or rigidity of muscles when they are at rest. Essentially, its function is to make your muscles feel rather strong during rest while not deliberately tensing them. Any amount of firmness you feel in your muscles while they are at rest without muscle tensing is the definition of muscle tone.
The Definition of Muscle Tone
There are two common muscle tone definitions. These include the real or accurate physiological definition, and the most common, traditional definition. Most people confuse muscle tone and muscle strength definitions.
Currently, if you find people with a toned body, you might think their muscles have an excellent visible appearance. In this sense, their muscle tone appears desirable only because it looks healthy. However, the real physiological definition of muscle tone is the normal state of balanced tension of the muscles or low-level contraction or rigidity of your muscles when they are at restful state.
Apart from maintaining posture and balance, your muscles get you ready for action, produces energy that keeps healthy muscles, and provides quick, unconscious reflexes to any immediate internal or external stimuli.
Why is Muscle Tone Important?
Improved Posture
Specific exercises that focus on the abdominal and upper body muscles improve posture. Also, performing weight- enduring and low-impact exercises while standing can tone the muscles while strengthening the bones as well. They also alleviate stress on the spinal cord and decrease the risk of osteoporosis.
Muscle Tone Leads to Improved Stamina and Reduces the Possibility of Getting Sick
In terms of health and function, muscle tone reduces body fat and weight. The decreased body weight on the body’s frame leads to better overall health such as benefits to the heart, the skeletal system, and the joints. Also, a toned body results in increased energy, more stamina, and better flexibility. You will also substantially decrease your risk of acquiring certain sicknesses, such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Improve your Mental Health
Research has indicated that people who exercise to tone muscles consistently have improved mental health, reduced stress levels, increased energy, and better self-confidence.
A healthy and well-toned body results in pleasant daily life experiences and activities.
Muscle Tone and Posture
A postural muscle tone is the stable muscles contraction required for holding different skeleton parts in the body in the right relation to the various and frequently varying attitudes and postures of the body. Consistent training improves muscle tones and creates excellent posture. Additionally, muscles develop better endurance and increase in size.
Muscle tone formed from regular exercise makes daily activities easier. Also, it prevents injury since good posture minimizes the strain on muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Good posture assists with sporting performance because unique positions are often crucial to victory; for instance, the position required to execute the golf swing.
People who have good posture or an upright body position are confident about themselves. Less confident individuals can often have their body language revealed from their slouched posture.
Muscle Tone and Sleep
Muscle tone is associated with REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, and it causes loss of tone in skeletal muscles. REM sleep takes place at intervals when a person is asleep and commonly characterized by rapid eye movements, more dreams, body movements, and quick breathing.
Skeletal muscles are usually not very active during REM sleep. It is the reason why they lose their tone which causes the muscles to rest during REM sleep. Also, it prevents people from producing movements during their dreams. However, all muscles do not lose their tone through REM sleep. For instance, the diaphragm, involved mainly for breathing maintains contraction. Eye muscles remain active, and even though the lids are closed, the eyes move from side to side during REM sleep, the reason where the name REM sleep originated.
Muscle Tone Physiology
The muscle tone physiology system mainly involves studies that are responsible for movement. Connected to the skeletal system includes approximately 700 named muscles that contribute almost half of the body weight of a person.
Each of these muscles is a separate organ made of blood vessels, nerves, skeletal muscle tissue, and tendons. Other body organs such as the heart, the blood vessels, and digestive organs also have muscle tissues in them. The function of the muscles in these organs is to transport substances throughout the body.
Skeletal muscles are not often flaccid or fully relaxed. Even though a muscle does not move, it contracts slightly to produce muscle tone and maintain its contractile proteins. The tension created by muscle tone enables muscles to stabilize joints continuously and maintain posture.
Muscle tone is achieved by an intricate interaction between the skeletal muscles and the nervous system. This process activates few motor units at a time, probably in a cyclical approach. Through this approach, muscles never get exhausted thoroughly, since some motor units can get better while others are active.
There are two types of muscle tones which include firm muscle tone and flaccid muscle tone.
Firm Muscle Tone
Your muscles consistently have a partial contraction, which keeps them healthy, secure, and ready for action each time. This muscle tone process is the only feature of skeletal muscle action that you cannot control willingly. Even for a relaxed muscle, nerve impulses from your brain trigger sets of muscle fibers within it to contract and maintain your muscle tone.
Flaccid Muscles Tones
If the nerve supply to a muscle gets destroyed, especially during an accident, its muscle fibers do not stimulate to contract in this method. This process will make the muscle lose its tone and be flaccid. Soon the muscle will begin to weaken.
Changes in muscle tones can also lead to diseases which include hypotonia and hypertonia.
Muscle Hypotonia: Low Muscle Tone
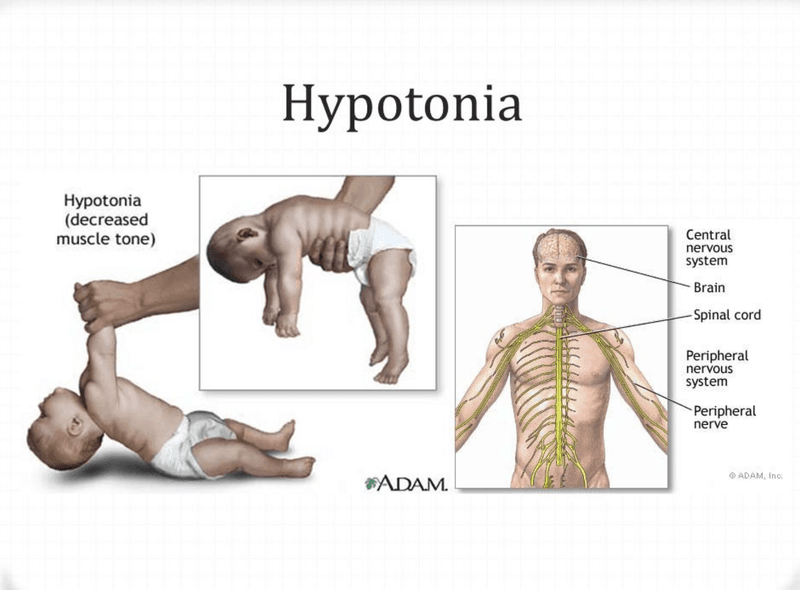
Hypotonia, also known as a floppy baby syndrome, is a condition that involves low muscle tone with reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific health sickness, but a possible sign of various disorders that affect muscle strength or motor nerve control by the brain.
What is Low Muscle Tone?
Low muscle tone mainly affects children who need a lot of effort to move their muscles properly during activities. Maintaining good posture is a significant problem when they sit or stand. Many children experiencing low muscle tone have slow gross motor development such as walking, sitting, and rolling. Low muscle tone can arise due to problems with the muscles and nerves. This disorder has no known cause.
Low Muscle Tone in Babies
Low muscle tone in babies often describes a child who has floppier, less rigid muscles than what is usually standard for children their age. Children with low muscle tone often need to put in more effort to get their muscles moving especially when they are doing upright activities.
Babies with low muscle tone frequently struggle with their posture and movement. Since when they begin an activity or movement their muscles are less tense, they often need to dedicate more effort to move their muscles while they perform activities.
The main symptoms are poor posture, increased flexibility, and a tendency to get tired quickly. One way of improving muscle tone in children is by using warm-up activities every day to activate the muscles.
Causes of low muscle tone include interference to the nerve pathways in the central nervous system (CNS) that are in control for switching on or off muscle activities. These nerve pathways transmit information from the CNS throughout the body to control posture and muscle tone. When damage occurs to these CNS nerve pathways, it leads to the disruption of messages from the brain to the body causing muscle tone abnormalities.
Low tone muscle is often common in children or adults who have experienced a stroke, cerebral palsy, or a severe head or spinal cord injury.
Symptoms of movement difficulties in children with low muscle tone include:
- Late attainment of the essential motor goals such as standing, sitting, standing, walking, and crawling.
- Some have difficulty or lateness in achieving higher motor skills levels such as hopping, jumping, skipping, using staircases, climbing and playing on field equipment.
- Ineptness. The children might fall more often than normal ones. They may also injure themselves more often.
- Poor posture includes several general examples such as preferring to lie on the floor, slumping or leaning on one hand especially when writing or drawing at a table. Others might stand with their belly protruding.
- Some may complain of pain in the legs or feet while exercising or walking. During the night, they may experience pain in the legs and knees.
- They have poor endurance and get tired very quickly, and they hate walking very far. Others prefer to be carried by their parent more often than others their age.
- Other children have complications with drawing and handwriting such as holding their pen with a firm grasp leading to quick hand exhaustion. For instance, their writing begins by appearing neat but after some few lines it appears sloppy, and they change the grip of the pen more often to manage the fatigue.
- They have difficulties controlling their mouth and jaw. For instance, this can include continuously opening their mouths while drooling and when concentrating. Some children experience problems progressing when they start chewing food and learning how to talk.
Muscle Hypertonia: Excessive Muscle Tone
What is Hypertonia?
Muscle hypertonia is an increase in the rigidity of muscle tone and reduced capacity of the muscle to stretch brought by injury to the CNS (central nervous system) or spinal cord causing disruptions in the nerve pathways in charge of muscle tone.
In children under the age of two, when the injury occurs, the most common term used for hypertonia is “cerebral palsy.” Hypertonia also may result from conditions such as spasticity, rigidity, or a combination of factors. It can also arise from dystonia which is extended muscle contractions that cause repetitive movements twisting and abnormal posture.
The symptoms associated with hypertonia include;
- Stiffness in muscles
- Loss of function
- Tenderness and pain in the affected muscles
- Decreased range of movement
- Spasticity of muscles
- Deformity
- An involuntary crossing of legs
- Rapid muscle contractions
- Fixed joints
The symptoms of hypertonia can differ significantly in severity attributes between people. It may affect only one part or both parts of the body. How these symptoms occur is highly dependent on the damage location that has happened within the spinal cord or the brain.
The most effective method used to treat and decrease the symptoms of hypertonia includes physiotherapy. Usually, physiotherapists can provide evaluation and treatment options which may include muscle stretching and techniques to assist in normal movement.
If left untreated hypertonia can cause contractures leading to malformation and loss of function.
What is Spastic Hypertonia?
Spastic hypertonia means hardening or straightening out of muscles, uncontrollable muscle spasms, shock-like contractions of part or all of a group of muscles, and uneven muscle tone. Common sicknesses associated with spastic hypertonia include stroke, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injury.
During diagnosis, your health provider will assess your medical history to identify spasticity hypertonia. The health provider will investigate the medications you have used and if you have a history of muscular and neurological disorders including your family. Several other tests can assist in confirming the diagnosis. These tests will assess your muscular activity, arm and leg movements, active and passive range of motion, and ability to do self-care activities.
Treatment may include medications such as baclofen, diazepam clonazepam, dantrolene, tizanidine, among others. Physical therapy activities that involve stretching of muscles and range of motion exercises may prevent tendon shortening. Rehabilitation can decrease or soothe the severity of symptoms and to boost functional performance.